Naive Bayes Algorithm
Published:
Naive Bayes Algorithm
- Basically, this is my studying from NTCU open course - Machine Learning. I take the key points for my references.
Bayes’ Rule
Assume that ${B_i, i=1,\dots,n}$ is a partition of $S$ such that $P(B_i)>0 \text{ for } i=1,2,…,k$. Then
\[\begin{aligned} P(B_j|A) &= \frac{P(A|B_j)P(B_j)}{P(A)}\\ &=\frac{P(A|B_j)P(B_j)}{\sum_{i=1}^kP(A|B_i)P(B_i)} \end{aligned}\]The Bayes’ Classifier
\[P(C_i|x)=\max\limits_{k} p(C_k|x)\]- For choose $i$ such that $P(C_i \vert x)$ is maximum is irrelevant with the value of $P(x)$.
Naive Bayes Algorithm
- Two not reasonalbe assumptions
- The importance of each of attribute is equal
- All attributes are conditional probability independent.
Likelihood Function
- ex. a baised coin flip $N$ times, and we could use MLE(Maximum Likelihood Estimates) to estimate the probability $p$ of coin with positive side.
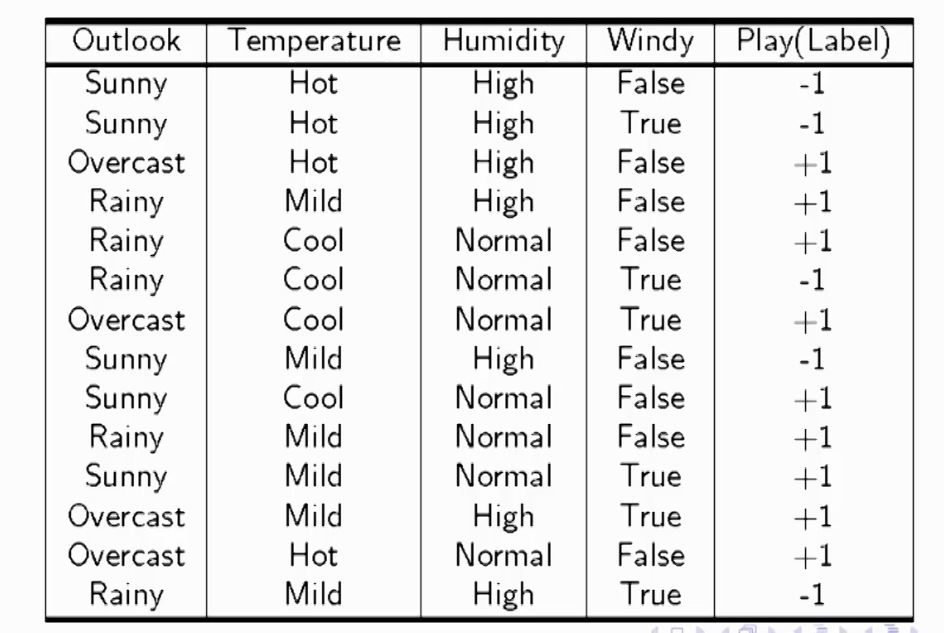
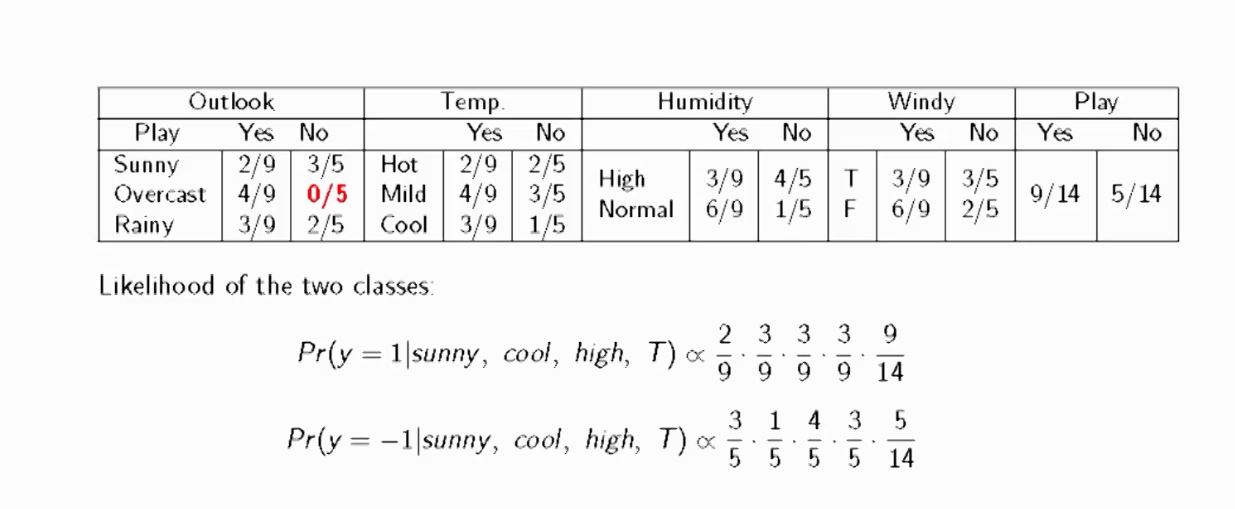
Example
- The above images are captured from link
python code
- This is from website
weather=['Sunny','Sunny','Overcast','Rainy','Rainy','Rainy','Overcast','Sunny','Sunny', 'Rainy','Sunny','Overcast','Overcast','Rainy'] temp=['Hot','Hot','Hot','Mild','Cool','Cool','Cool','Mild','Cool','Mild','Mild','Mild','Hot','Mild'] play=['No','No','Yes','Yes','Yes','No','Yes','No','Yes','Yes','Yes','Yes','Yes','No'] - Encoding Features
# Import LabelEncoder from sklearn import preprocessing #creating labelEncoder le = preprocessing.LabelEncoder() # Converting string labels into numbers. weather_encoded=le.fit_transform(weather) print weather_encodedtemp_encoded=le.fit_transform(temp) label=le.fit_transform(play) print "Temp:",temp_encoded print "Play:",label features=zip(weather_encoded,temp_encoded) print features - Perform prediction
#Import Gaussian Naive Bayes model from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB #Create a Gaussian Classifier model = GaussianNB() # Train the model using the training sets model.fit(features,label) #Predict Output predicted= model.predict([[0,2]]) # 0:Overcast, 2:Mild print "Predicted Value:", predicted